
Adviser:
Amitabha Mukerjee
Abstract
 |
 |
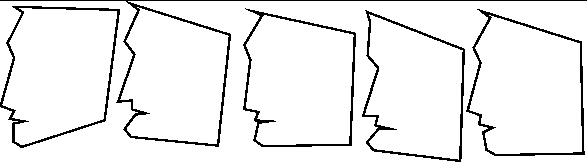
| Variational shape classes. Top: 2% vertex variation. Bottom edge length and angle variation (5,10%). High variation contours are particularly difficult to recognize when they are partially overlapping. |
Many shapes are not exact, and can vary to differing degrees. A shape class captures this extent of variability. The main contribution of this thesis is formalising a theory of shape class modelling. We provide two methods of deformational shape class modelling. We use a novel polygonal representation scheme with local invariant relations of edge vectors with supersegments. This is translation, rotation and scale invariant which saves us from a searching for appropriate transformations for the candidate models. This model of representation is can be made very stable under varia- tions using higher length supersegments.
We venture with three algorithms for identification of variational shape classes with supersegment matching strategy:
As the title portrays, all the three algorithms are capable to identify
partially visible shape classes from a given image.
 |
 |
 |
Occluding Image Contours. Two animal shapes overlapping by increasing degrees. All three cases are recognized by the maximal supersegment model. | ||
Goswami, Anjan; and Amitabha Mukerjee; 1999.
Modeling and recognition of Planar Shape Classes,
Proceedings Fourth Intl Conf on Advances in Pattern Recognition
and Digital Technology, Calcutta, December 27-29,
1999. [ gzipped Postscript, (82696 bytes) ]
Goswami, Anjan; and Amitabha Mukerjee; 2000
Multi-Threshold Hausdorff Distance with Maximal Arc-Length
Matching for Variational Shape Recognition,
ECCV-2000, Dublin Ireland, June 2000. (under review). [ gzipped Postscript (82 kB) ].