|
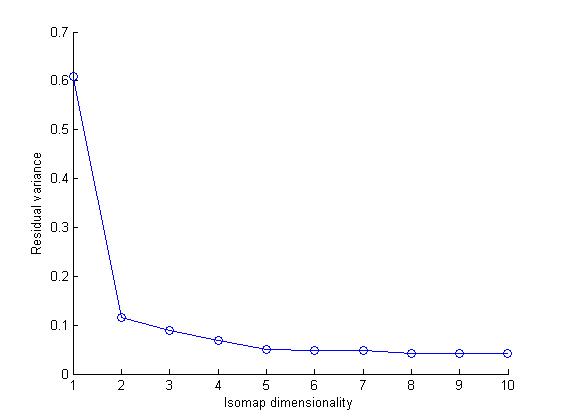 |
We can observe that there is a sharp kink at dimensionality equal to 2. |
|
 |
We can observe that there is a sharp kink at dimensionality equal to 2. |
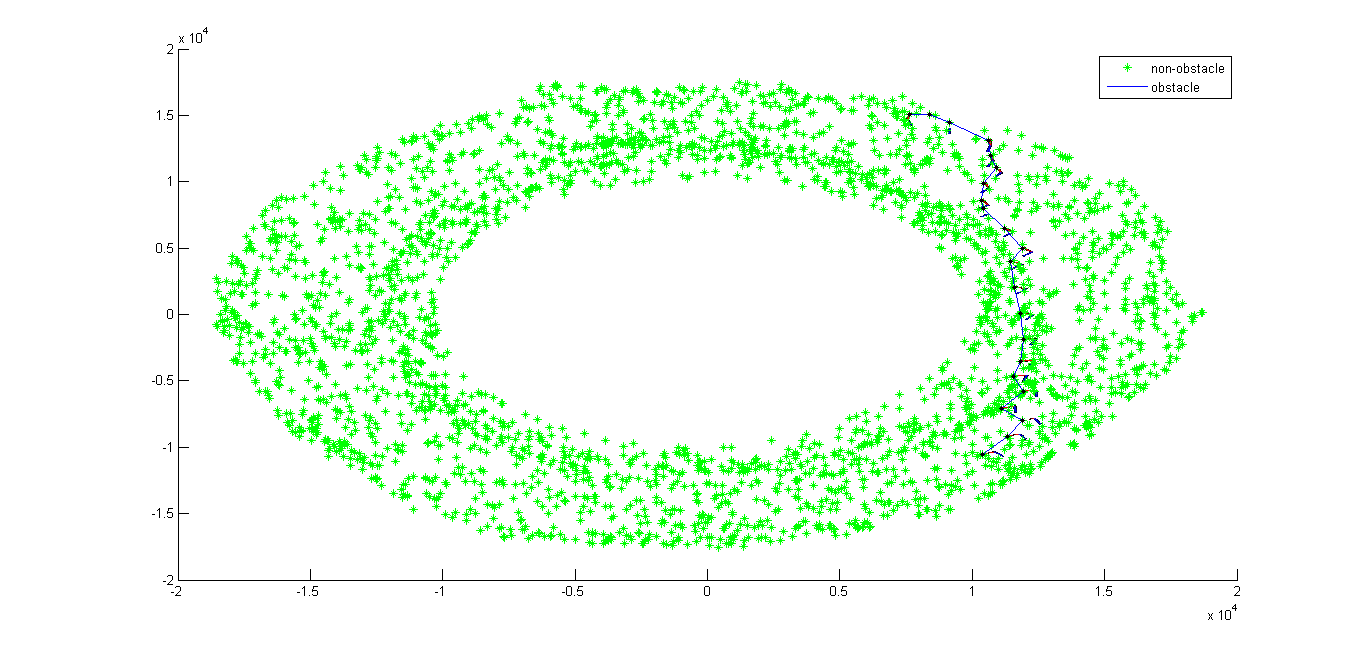
2-D embedding when k=5 using Isomap.m |
 |
2-D embedding when k=5 using Isomap.m |
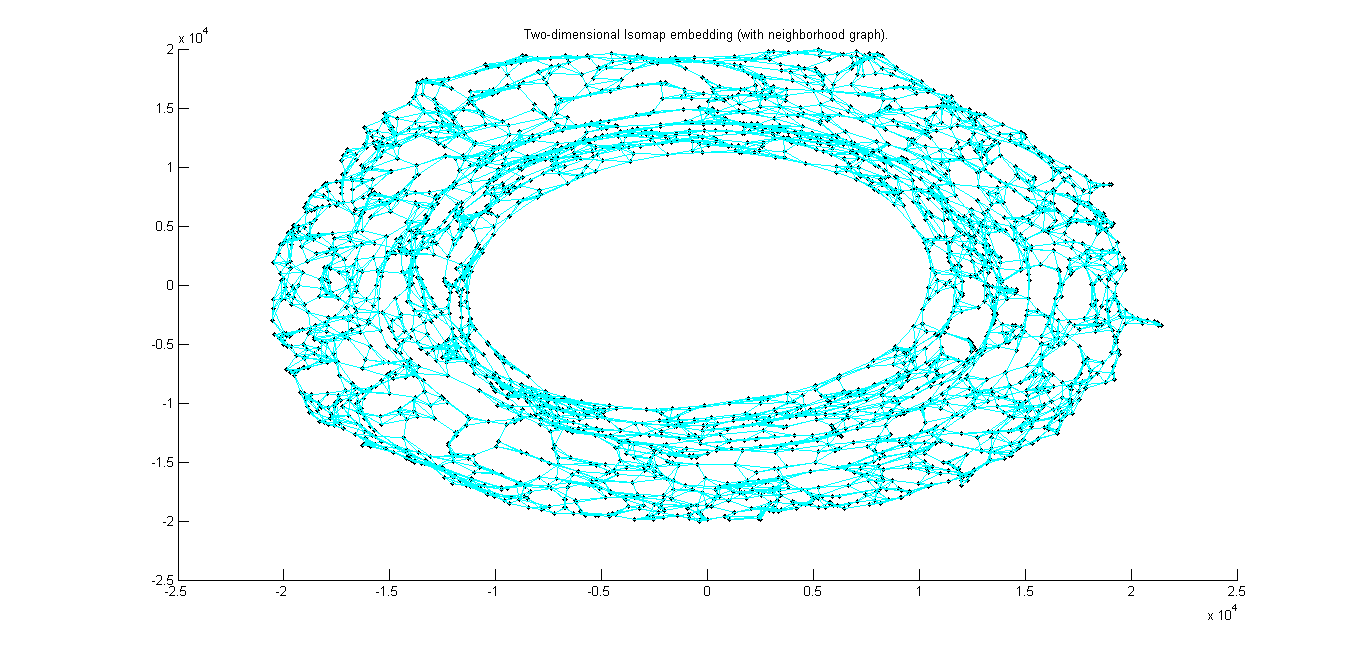 |
|
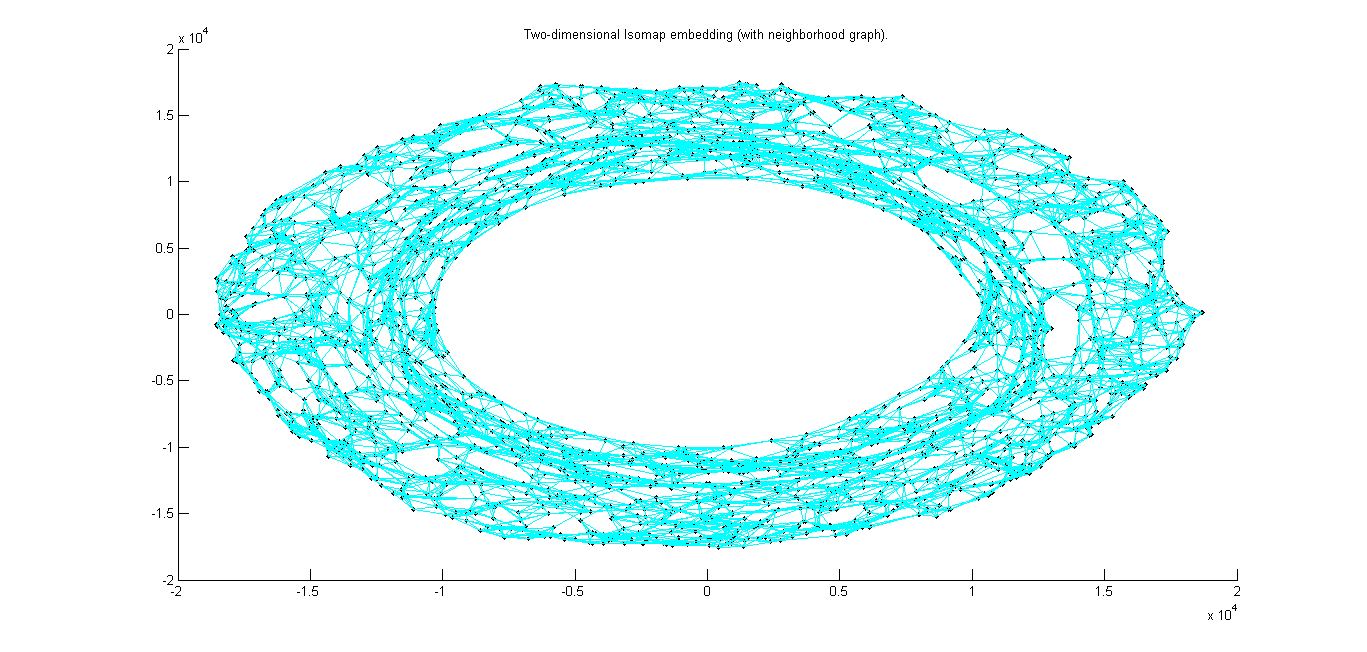 |