Homework 3
Submission By: Akshay Agrawal & Maninderjit Singh
(10058 & 10381)
Complete assignment(including all the neccesary codes and relevant data) can be found here
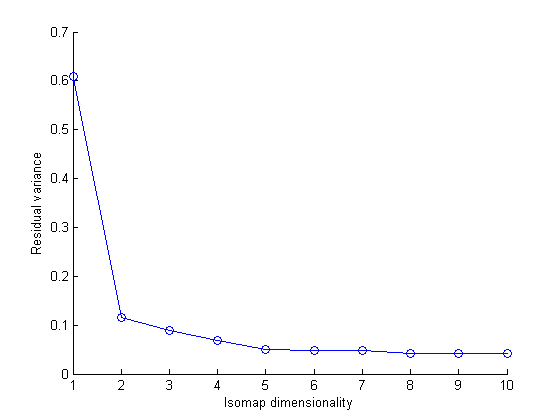
A.) Dimensionality determination:
A steep fall occurs while going from dimensionality 1 to 2, thus Dimensionality of this manifold of images is 2.
B.) 2-Dimensional Embedding:
C.) Zoomed view of an area of this 2-dimensional manifold:
Red rods have almost a similar inclination in a small region
Blue rods have varying inclinations corresponding to similar regions of red
Implies for a given "theta 1" values, "theta 2" shows a complete 360 degrees variation which can be more clearly visible in a 3-d isomap
D.) Embedding in 3D space:
E.) Network training:
a. Training network from 2-d parameters to control parameters using Multi Layer Perceptron
b. Training network directly from images to control parameters using Multi Layer Perceptron
a. Training network directly from images to control parameters using Neural Network having 1 hidden layer with 10 neurons
Training the same Neural Network for images, caused "OUT OF MEMORY" error, irrespective of how greatly the image was compressed
Convergence:
- Approach 1, of first producing the isomap and then mapping the parameters from this 2-dimensional space to control space is faster
Reason:
- Dimensionality reduction eases the training job, as networks are to be trained from 2-d input parameters to 4-d output parameters
as compared to direct mapping, where a network is needed to be trained for input vector of order of "10,000"'s to 4-d output parameters
- Dimensionality reduction is slow but still consumes lesser time and memory as compared to the direct network training approach
c. Shortest path from node "1" to "161" in this 2-dimensional isomap
F.) Path plan on the attenuated graph-1
G.) Path plan on the attenuated graph-2
Difference between above two path finding problems:
In part (i) a complete sector of the torroid gets removed from the final embedded space thereby leaving a longer route,
(shifting "theta1" along
anti-clockwise direction), while in part(ii) only a small section gets removed from the torroid,
thus allowing a shortest path along clockwise direction itself.