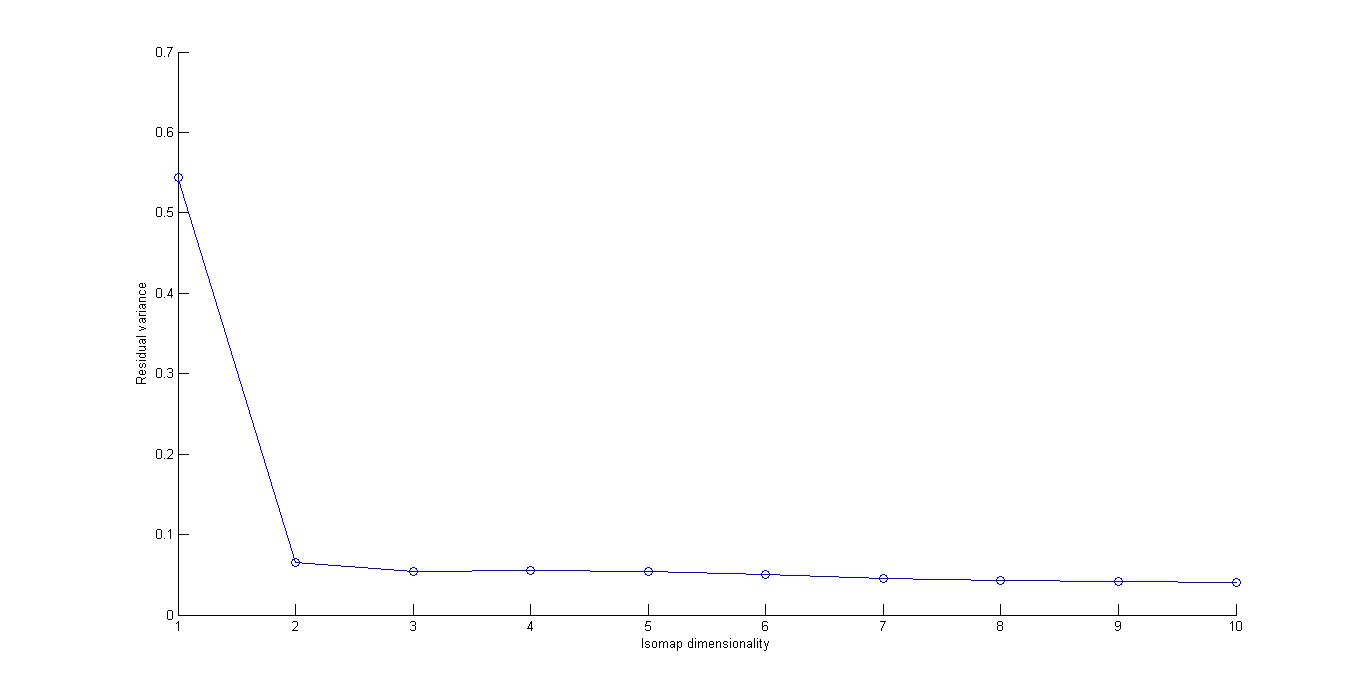
We can clearly see from the residual variance plot that there is a sudden decrease in the residual variance on moving from dimensionality 1 to 2.However on increasing the dimensionality we see that there is no significant change in the residual variance.Hence we can say that the dimensionality of manifold is best explained at 2
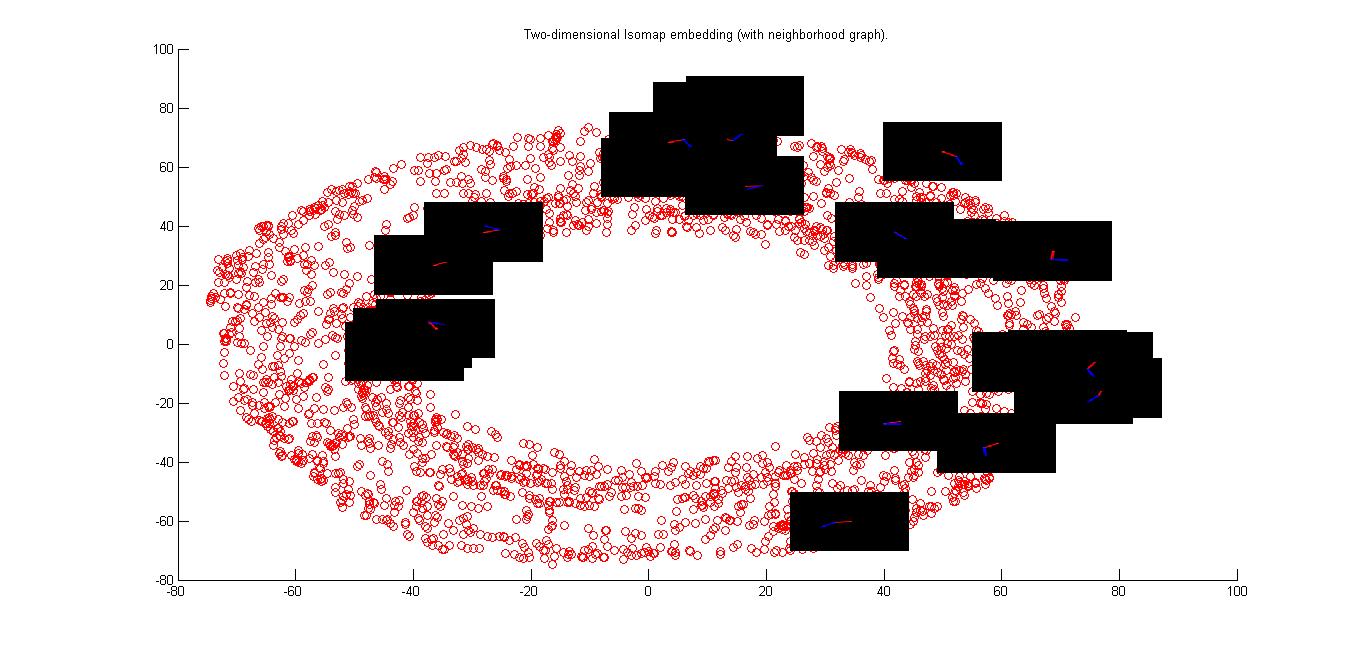
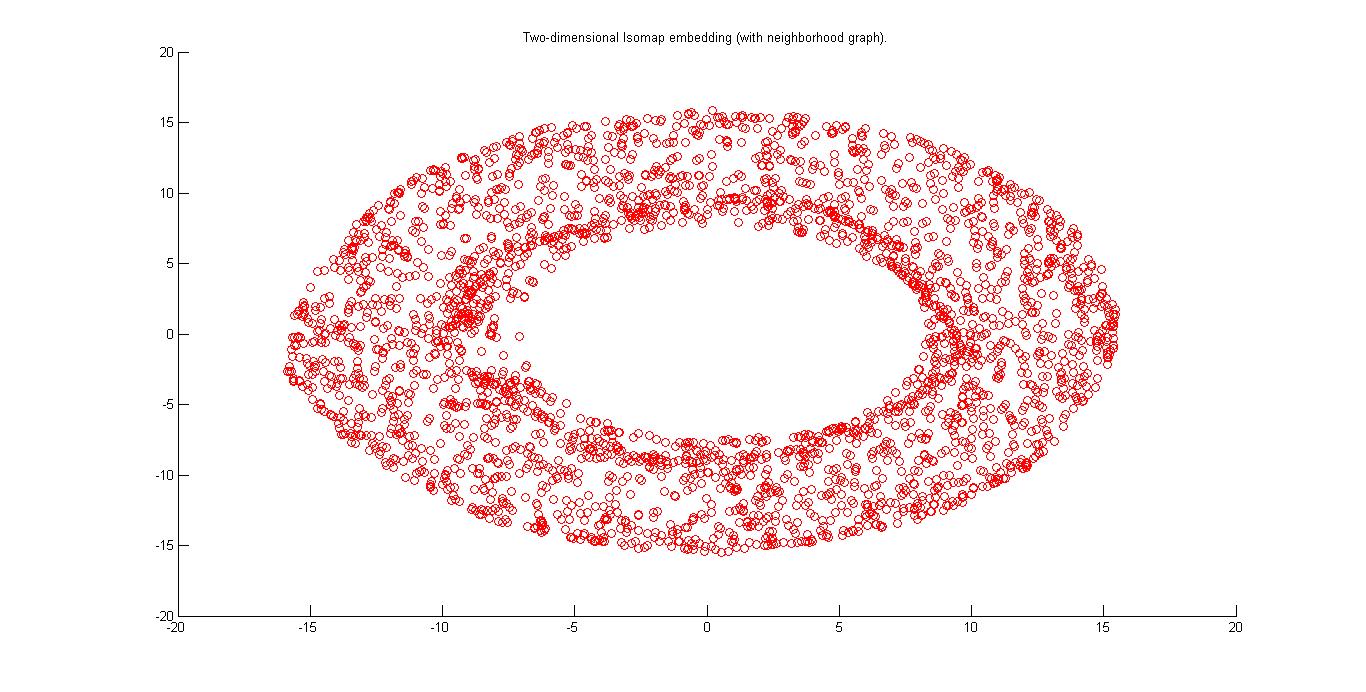
In this figure a 2D isomap of a torus is shown which is generated by the free movement of hand given in the question.

In this fgure I have fixed one value for theta1 and all the images with same theta1 and different theta2 are shown in the red dots.
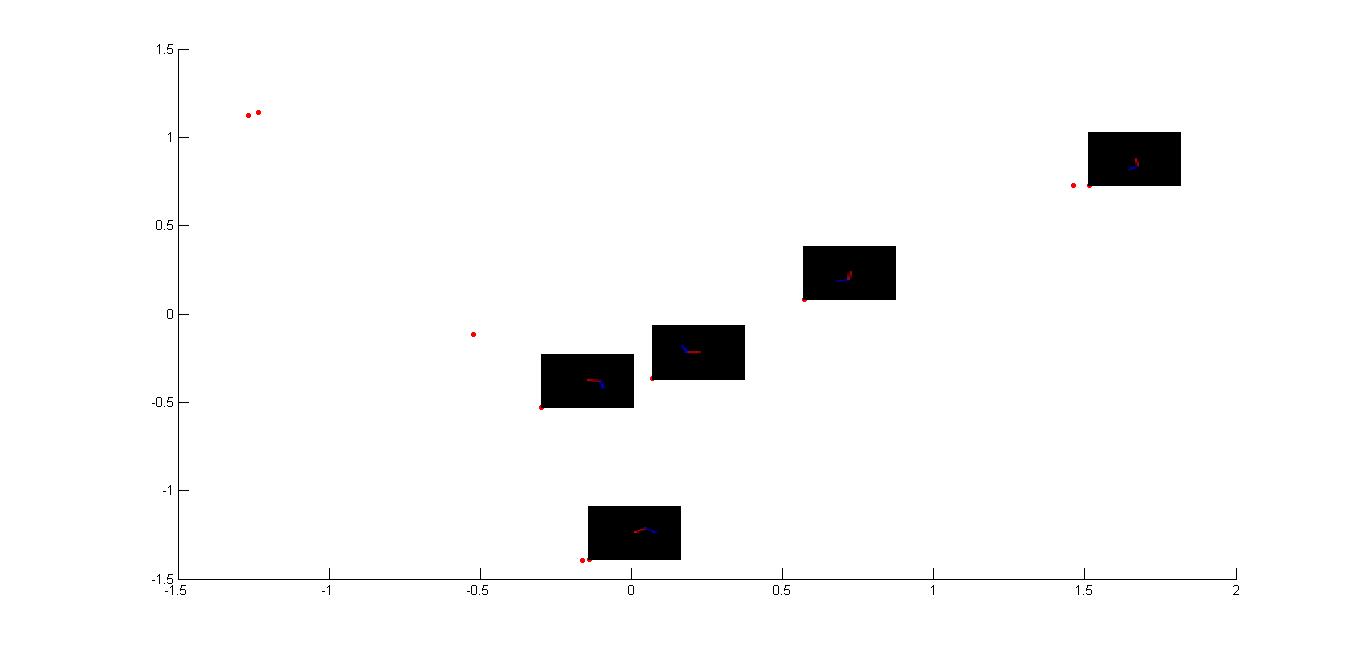 In this fgure I have fixed one value for theta2 and all the images with same theta2 and different theta1 are shown in the red dots.
In this fgure I have fixed one value for theta2 and all the images with same theta2 and different theta1 are shown in the red dots.

This is a figure which is 3D isomap embedding of the free hand. Topology is that of a toroid.

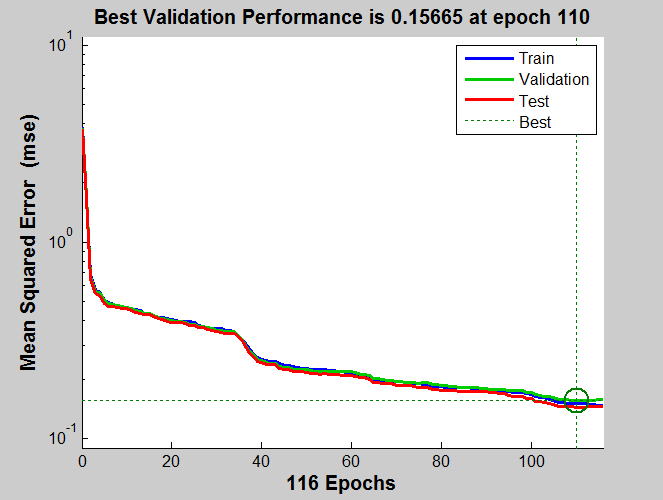
we can say that learning the map from 2D parameters for the robot converges faster than using control parameters. This is because of the less dimension of the input parameter in the first case which is 2 than the second case which is 4. So it takes lesser time by using 2D parameters.
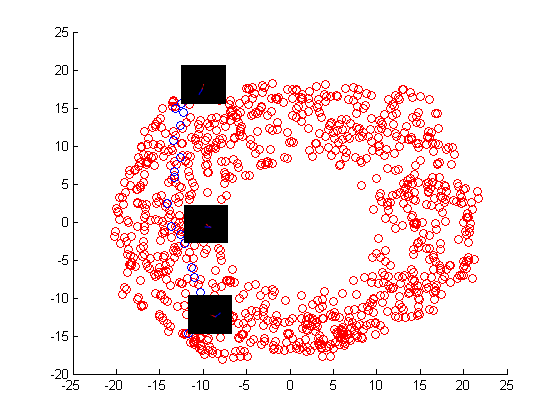
In this above figure I have shown the shortest path (nodes in the blue color) between node corresponding to the image 1 and node corresponnding to the image 161.
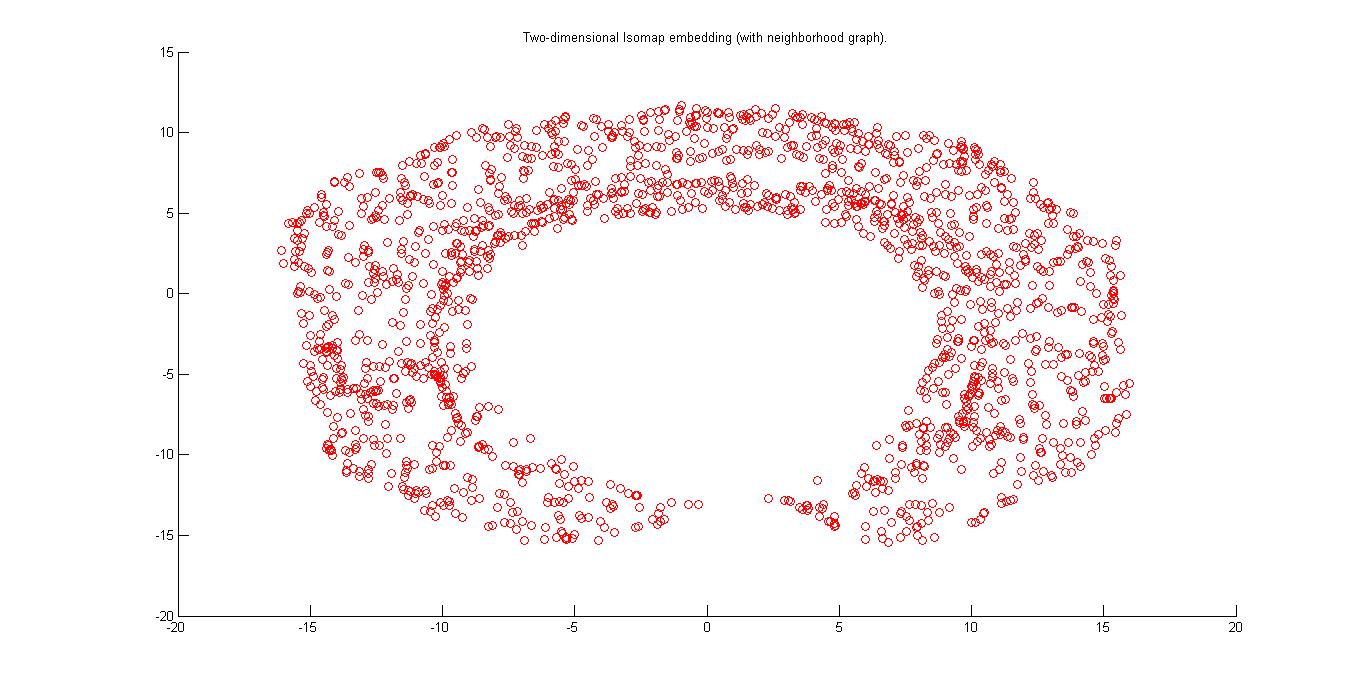
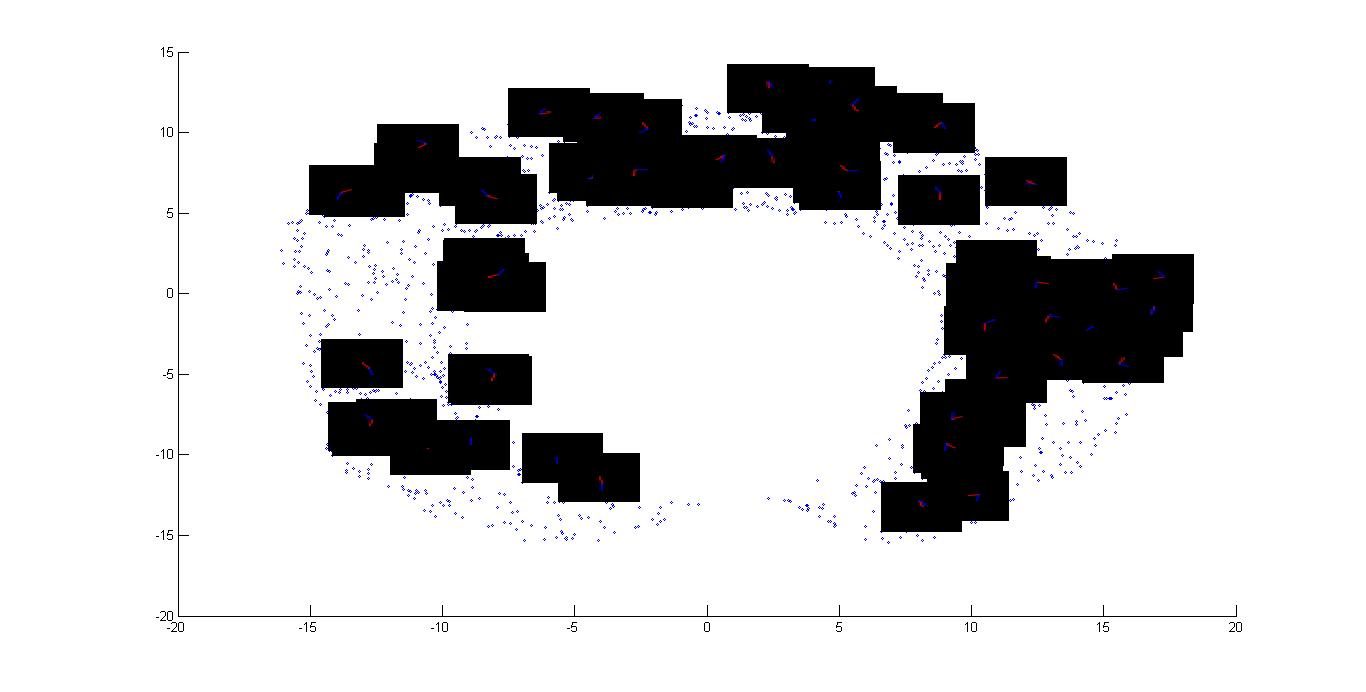
In the above images I have removed all the nodes from the graph, shown in the part B, in which hand is colliding with the obstacle1. First figure is showing only the nodes in the graph. In the second figure I have put somes images on the corresponding node on the plot.
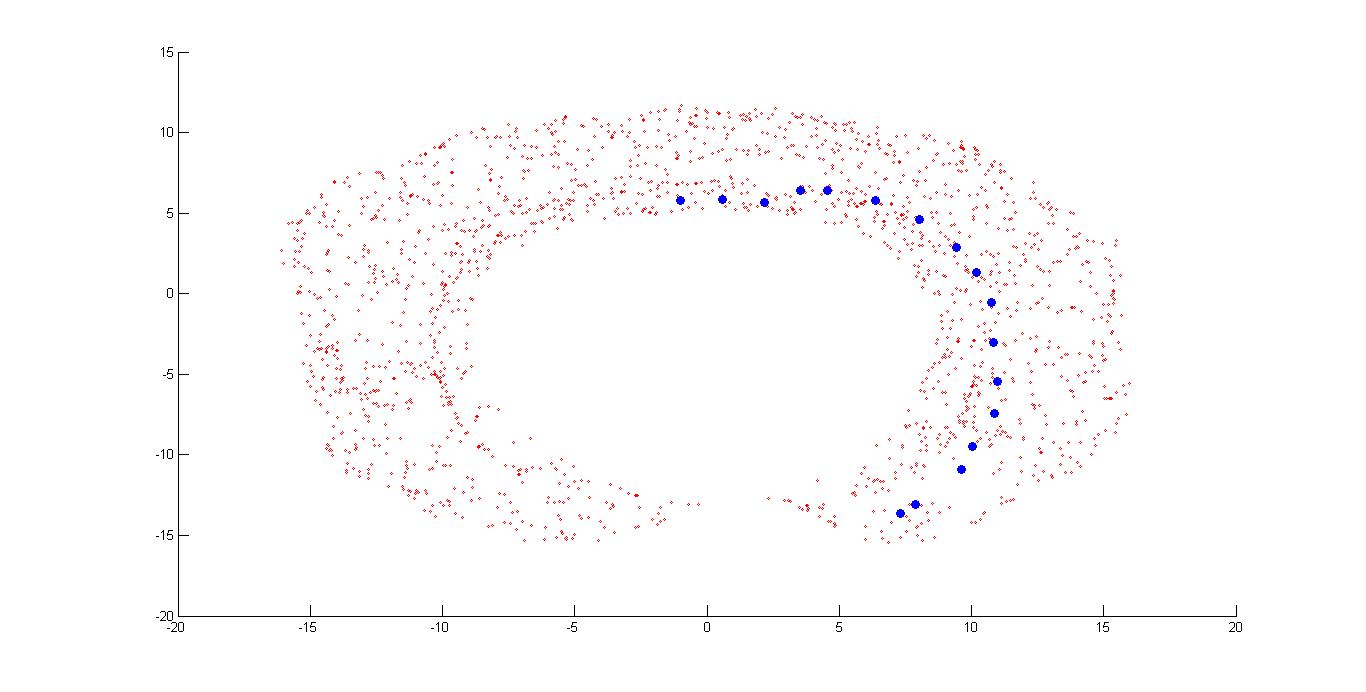
In this fgure I have shown the shortest path between node corresponding to the image 1 and node corresponnding to the image 161 by using only those node which are present in the graph after removing those nodes in which hand is colliding with the obstacle1.
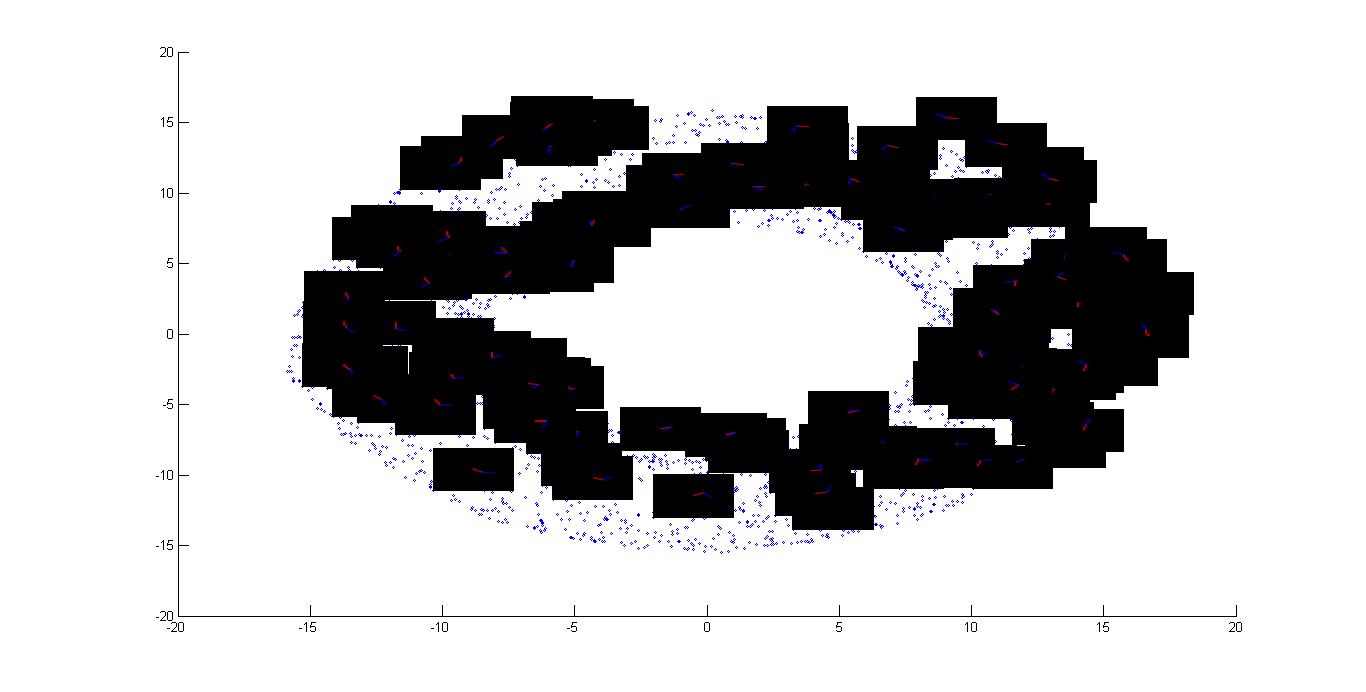
In the above images I have removed all the nodes from the graph, shown in the part B, in which hand is colliding with the obstacle2.
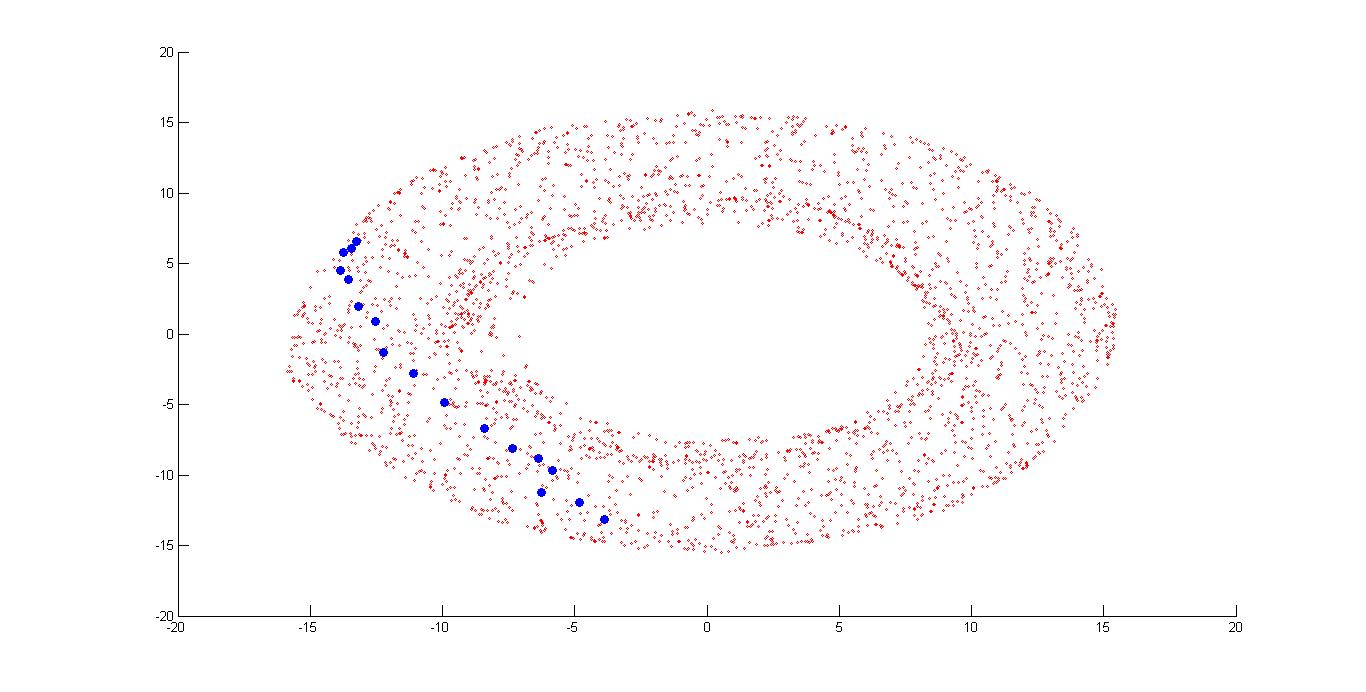
In this fgure I have shown the shortest path between node corresponding to the image 1 and node corresponnding to the image 161 by using only those node which are present in the graph after removing those nodes in which hand is colliding with the obstacle2.