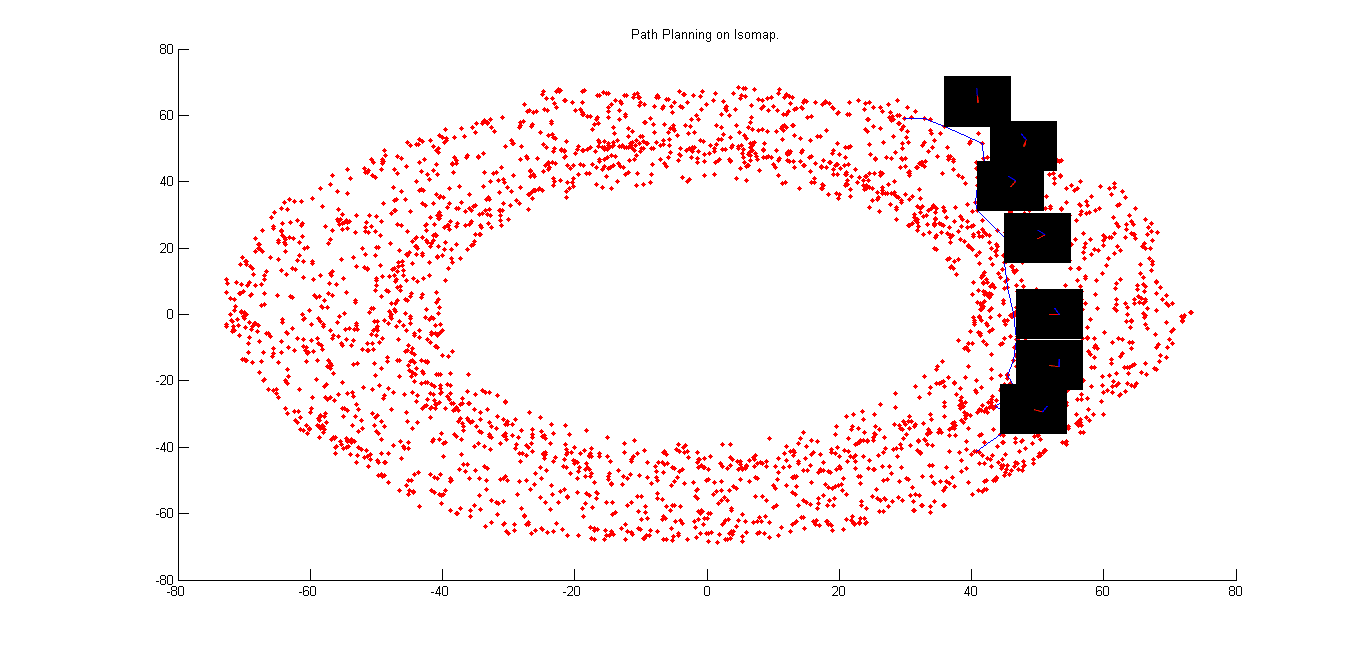
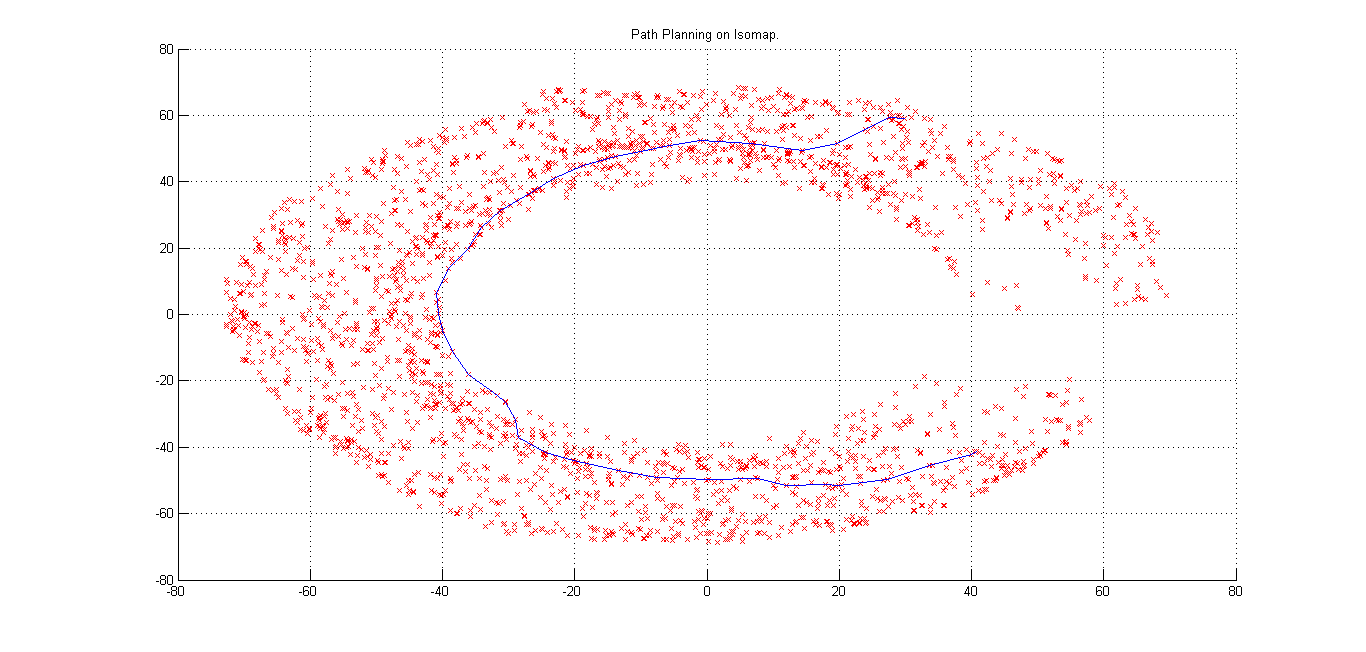
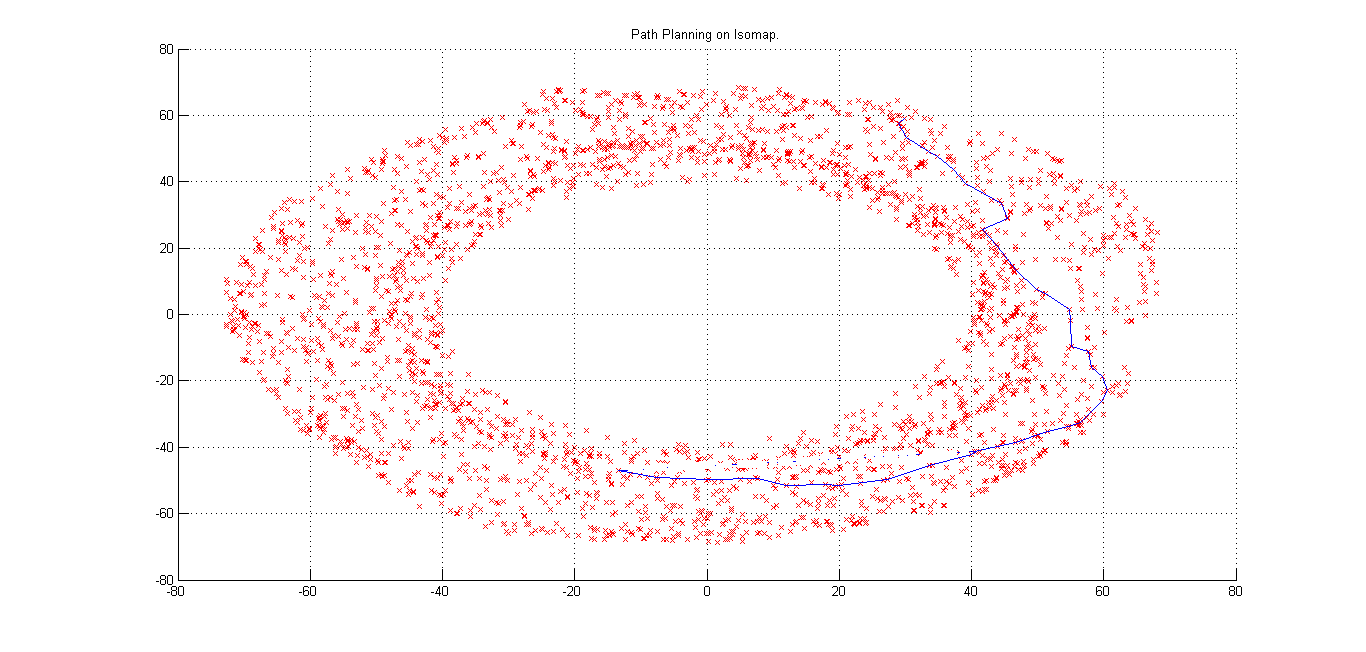
The figures below show the 2D Isomap Plot and residual variation with dimension. As evident from the residual graph, we can see that maxium residual variation is corresponding to dimension '2'. From this we infer that dimensionality of the manifold is best explained at '2'.

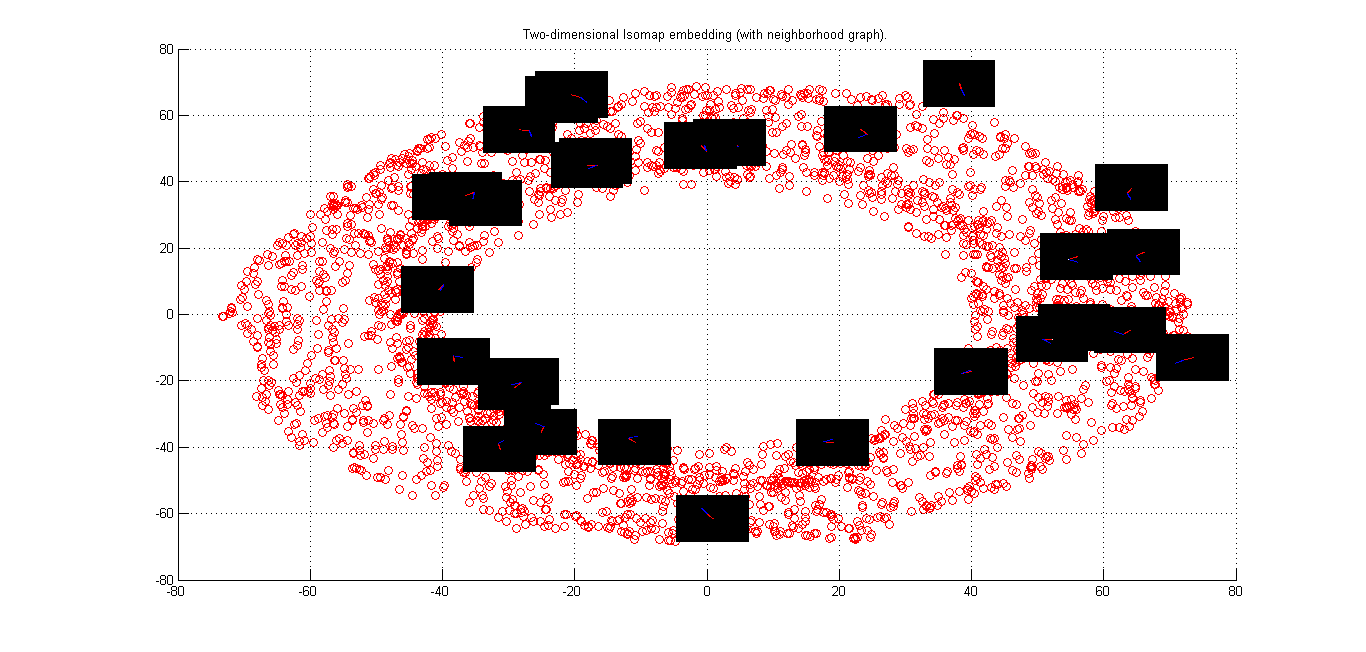
Following figure shows the variation of Theta1 over the manifold. Moving along a circle centered at origin theta1 varies from 0 to 2 pi.
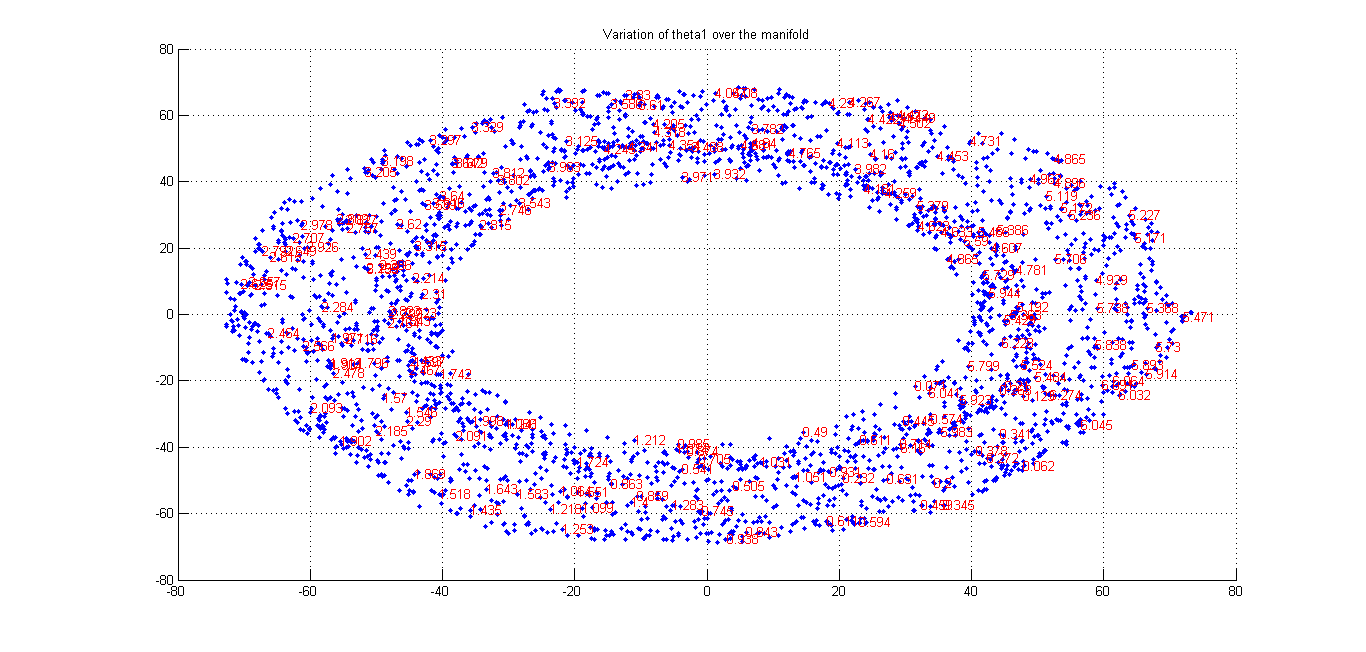
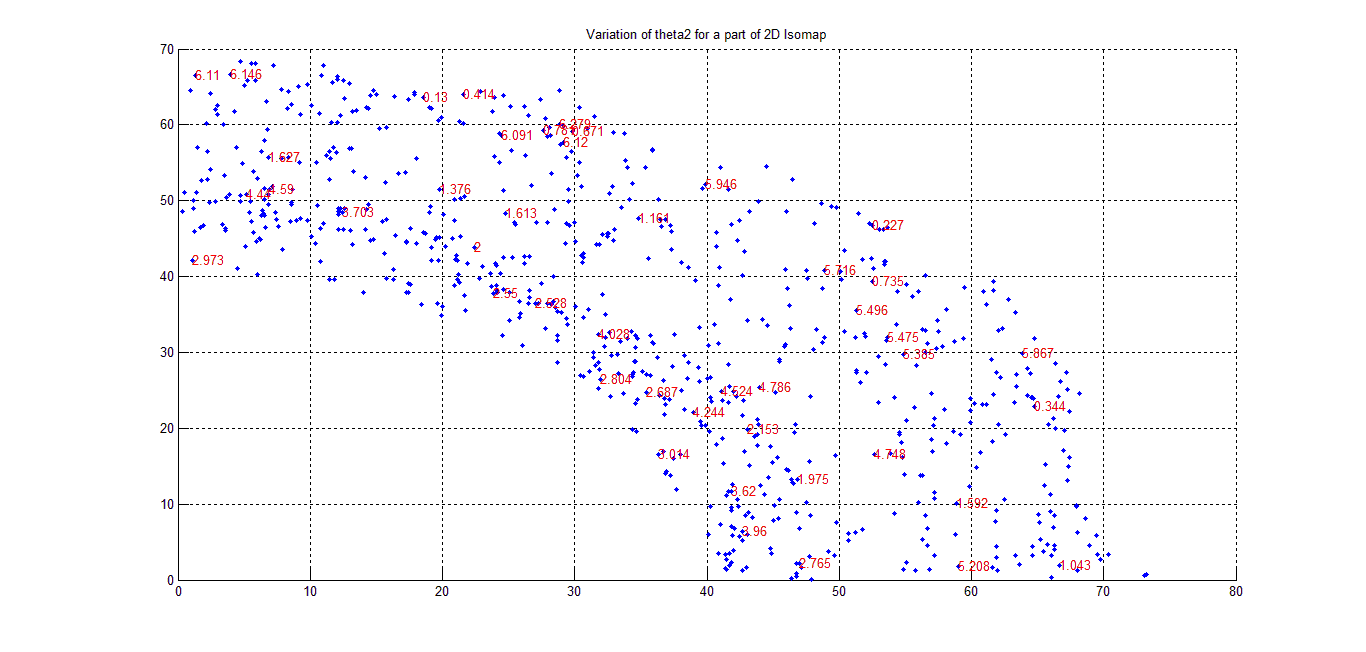
Following figure shows the variation of Theta2 over a portion of 2D-manifold. The values of theta2 have been writen on the plot (not all points to keep the figure clear). Moving radially we find theta2 varies -pi to +pi.
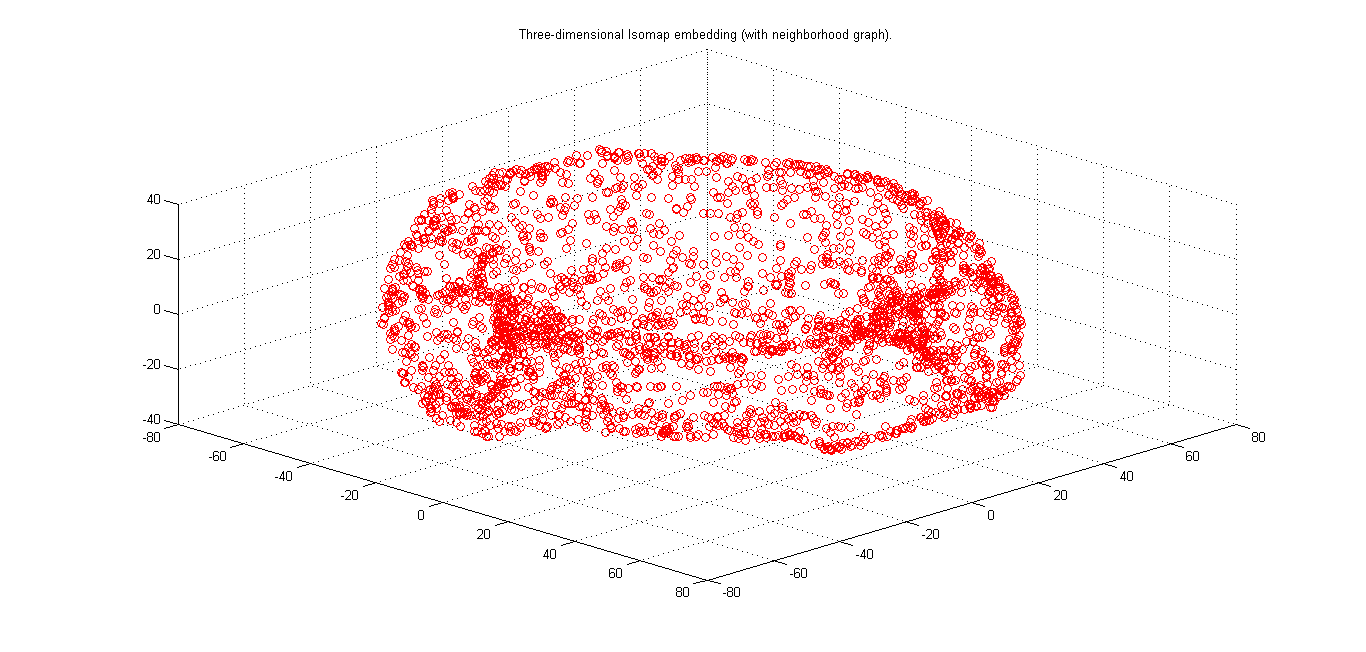
From the 3 Dimensional plot we can see that the topology followed by the robotics arm is of a "TOROID".
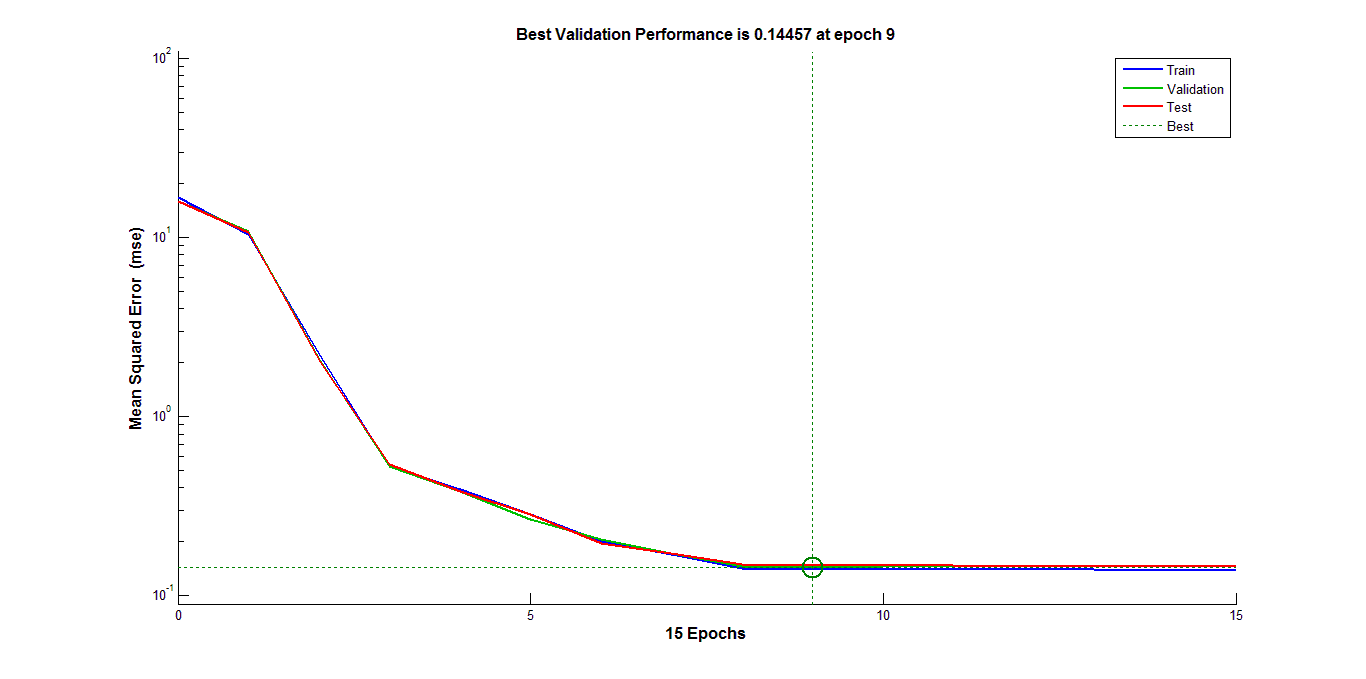
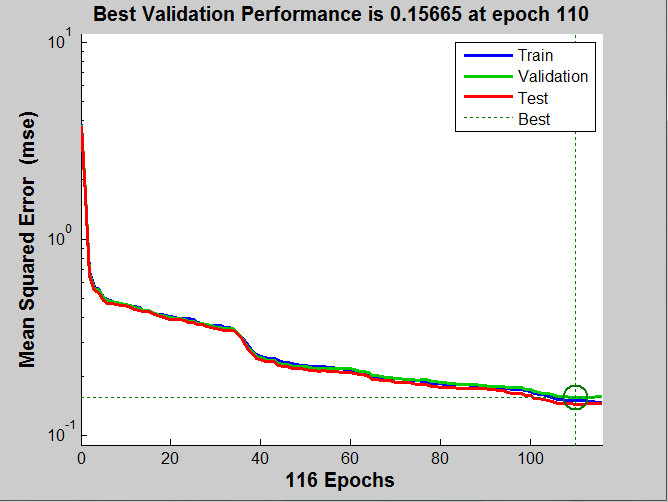
As evident from the following two figures we can see that larning the desired mapping is faster in case we learn it from 2D Isomap manifold because it converges faster. But when we train with images directly, the number of epochs required are much larger as compared to previous method because we are working in a very high dimension and number of training examles is also less with respect to the nubber of features. The first graph correspond to training from Isomap manifod. The second graph correspond to training directly from images.